wood pellets how to make ,Woody materials include branches, logs, chips, shavings, and other waste wood. agricultural waste such as crop stalks, alfalfa, bamboo, rice husk, sunflower husk, peanut shell, EFB palm fruit bunch and so on.
Others include activated carbon, sugarcane bagasse, coconut shell, bamboo, cow manure, EFB, cement, ash, fertiliser, chemicals, etc. The YuFChina Ring Die Pellet Mill is capable of processing a wide range of raw materials, including wood sawdust, coffee, peanut, and rice husks, grass, bamboo, palm, sugar cane, straw, activated carbon, sludge, and so on. Even for very hard materials and unique requirements for the line, we have solutions.
wood pellets how to make
There are various procedures involved in making wood pellets at home, as well as specific equipment. This is a condensed synopsis of the procedure:
Reduce wood into small pieces: You can use a chipper, grinder, or hammer mill to achieve this. The ideal size is around 3-5 mm.
How to produce wood pellets?
Control moisture content: Wood pellets require a specific moisture content (10-18%) for proper binding during compression. If your wood is too wet, you might need a dryer to bring it down to the appropriate level.
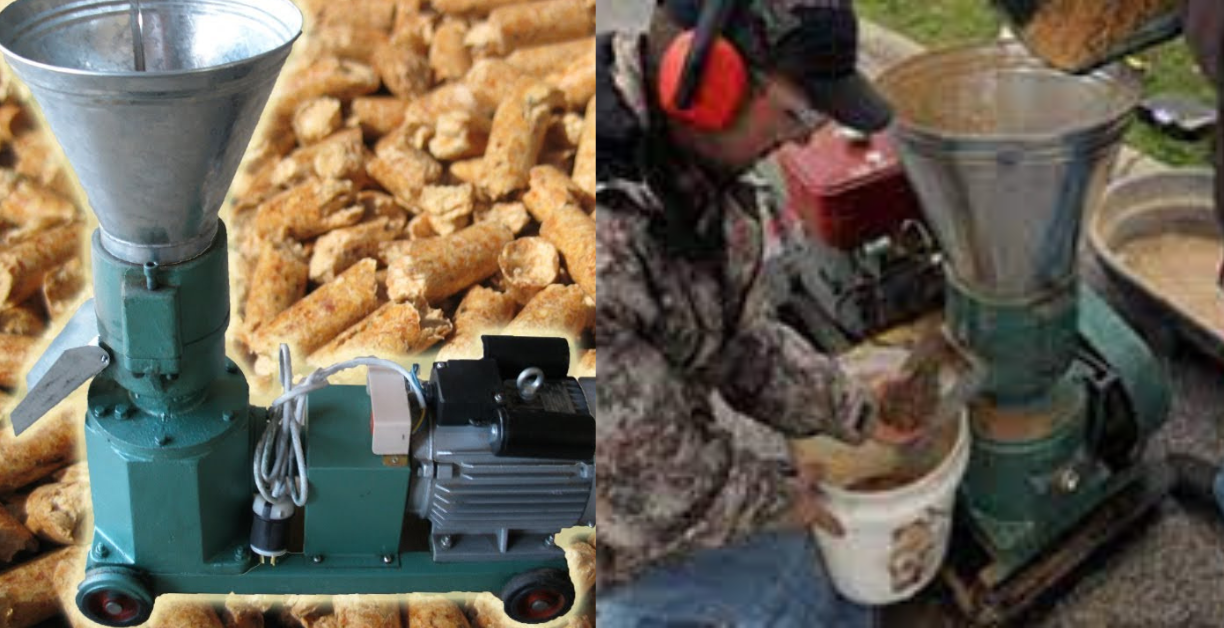
Pellet mill: This machine compresses the wood particles into dense pellets using a pressing force.
While it’s possible to make wood pellets at home, it’s generally more cost-effective to purchase them from a commercial producer, especially for small-scale use.
Crafting wood pellets at home involves several stages and necessitates specialized machinery. Here’s a more detailed breakdown of the process:
Wood Size Reduction: The first step involves reducing wood into small, uniform pieces. This can be achieved using a chipper, grinder, or hammer mill. The ideal size for the wood particles is around 3-5 millimeters, which ensures efficient compression during pelleting.
Moisture Management: Wood requires a specific moisture content, typically ranging from 10-18%, to create strong and durable pellets. If the wood is too wet, it may not bind properly during compression. Conversely, excessively dry wood can result in brittle pellets. In cases where the wood is too wet, a dryer might be necessary to bring down the moisture content to the optimal level.

Read more
how many lands should be in a landfall deck
how far away should you be from the steering wheel
why is cat litter so expensive
Pellet Mill: The core apparatus in this process is the pellet mill. This machine houses a die and rollers that compress the wood particles under high pressure. The intense pressure forces the wood to generate heat and lignin, a natural binding agent present in wood. This lignin melts and binds the wood particles together, forming the compacted wood pellets.
Cooling and Screening: Once compressed, the hot pellets are passed through a cooler to solidify the lignin bond and prevent spontaneous combustion. Finally, the pellets are screened to ensure uniform size and remove any oversized or undersized pellets.
Hope you clear wood pellets how to make. While creating wood pellets at home is technically possible, it’s generally more practical and economical to purchase them from a commercial producer, particularly for small-scale use. Commercial pellet mills are highly efficient and can produce large quantities of pellets at a faster rate. Additionally, commercial producers often have access to high-volume, low-cost wood sources, making the process more cost-effective.
What chemicals are used to make wood pellets?
Wood pellets are primarily made from sawdust and wood shavings, sourced from sawmills and lumber yards due to their high cellulose content and low moisture levels. Initially, the raw materials are collected and dried to reduce moisture content, a critical step for achieving the desired pellet density and quality.
Once dried, the sawdust and shavings undergo compression in pellet mills. During this process, the natural lignin present in the wood acts as a binder, bonding the wood particles together under high pressure and temperature. This natural binding process eliminates the need for additional chemicals in most cases, ensuring that wood pellets remain predominantly natural.
While sawdust and shavings are the primary components, some manufacturers may add small amounts of vegetable oil or other natural additives to enhance pellet performance. These additives can improve combustion properties, increase durability, or reduce dust formation during handling and storage. However, reputable manufacturers disclose the use of such additives and employ them sparingly.
Overall, the production of wood pellets prioritizes sustainability and environmental responsibility by utilizing wood residues and natural binders. This approach minimizes waste and reduces the environmental impact associated with traditional wood processing. By doing so, wood pellets continue to serve as a clean and efficient energy source for heating and power generation, supporting renewable energy initiatives.
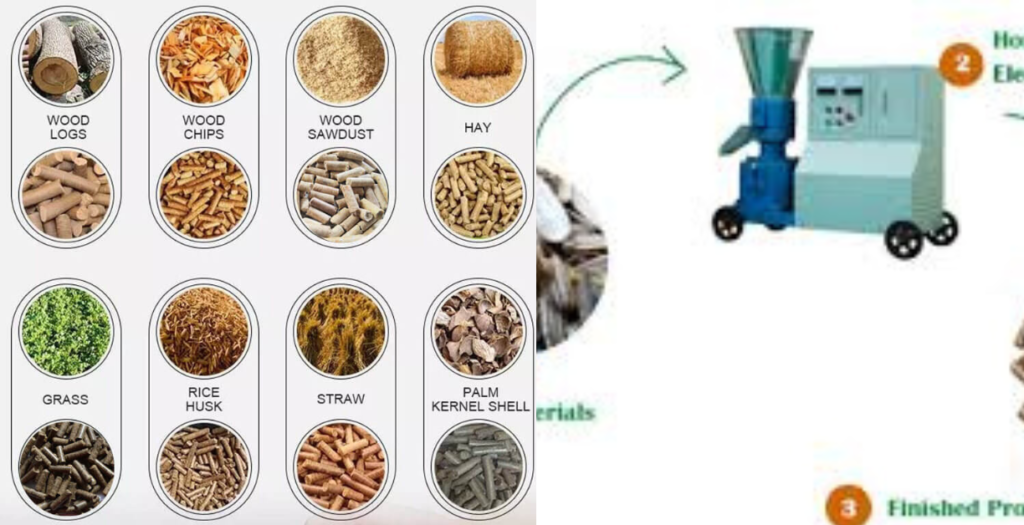
What are the materials used in pellet feed?
Pellet feed, widely used in animal nutrition, consists of various ingredients processed into compact pellets for easy consumption by animals. The composition of pellet feed varies depending on the animal type and its nutritional needs. Typically, pellet feed includes:
1. *Grains:* Such as corn, wheat, barley, and oats, which provide carbohydrates and energy.
2. *Protein Sources:* Like soybean meal, fish meal, meat and bone meal, and other plant or animal-based proteins essential for muscle development and growth.
3. *Vitamins and Minerals:* Essential nutrients such as vitamins A, D, E, B vitamins, calcium, phosphorus, and trace minerals (e.g., zinc, copper, selenium) crucial for health and metabolic functions.
4. *Fats and Oils:* Derived from vegetable oils or animal fats, offering concentrated energy and essential fatty acids.
5. *Fiber Sources:* Including alfalfa, soybean hulls, or other plant fibers aiding digestion and promoting gut health.
6. *Additives and Supplements:* These can be probiotics, enzymes, antioxidants, and other additives enhancing digestion, immunity, and overall well-being.
Manufacturers tailor pellet feed formulations to meet specific nutritional standards based on the animals’ growth stages and dietary requirements. By carefully balancing these ingredients, pellet feed supports optimal health, productivity, and performance in animals.















